A guide to drone surveying, deliverables, accuracy, and workflows
Drones are continually proving to be powerful commercial tools, simultaneously providing adopters with leaps in efficiency and safety. The surveying and mapping industry is no exception.
With their ability to capture data from above, drones have been successfully integrated into surveying workflows to perform land surveys, photogrammetry, 3D mapping, topographic surveying, and more.
Whether you’re an experienced surveyor looking to expand your toolkit, or you’re a drone enthusiast who wants to know more ways to use their drone, or you’re just generally interested in this awesome application of drones, we’ve put together an article to help you learn everything you need to know when it comes to getting started with drone surveying.
Phantom 4 RTK, an aerial surveying drone
What is a drone survey?
Surveying is the precise science of determining the positions of, and the distances between, points in 2D and 3D space. There is a big difference between aerial photography and surveying.
Surveys provide critical information that enables informed decision making ranging from construction site planning, to design and upkeep of infrastructure, to delineating cadastral property boundaries, and more.
A drone survey is simply a survey conducted from overhead using a drone.
Drone photogrammetry
Why is using drones for surveying superior compared to traditional methods?
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles, or UAVs, excel at rapidly acquiring data from vantage points inaccessible to humans.
When surveying challenging terrain, drones make it no longer necessary for human operators to physically access and measure points in hazardous or difficult-to-reach locations.
Additionally, while traditional surveying methods require meticulous measurement, preparation, and planning, drones can capture comparable data in dramatically shorter timeframes.
For example, STRABAG, a leading Austrian construction company estimates drones enable them to conduct surveys with 75% reduced GCP set-up time. Click here to learn more about STRABAG’s gains in efficiency.
In sum, drone surveying produces quality results quickly, profitably, and safely.
What kinds of deliverables can you achieve with drone surveying?
Depending on your choice of data sensors and surveying software, drone surveying can produce a variety of deliverables with use cases in many industries. Surveying software can stitch together hundreds or thousands of digital photos captured by your drone, and produce high quality 2D Orthomosaic maps.

- Large numbers of digital photos of your surveying site can be compiled into a 3D orthomosaic map and can provide actionable topographic data.
- Generate 3D models of targets in your surveying site for quick comparison with BIM
- Survey with a thermal camera and quickly identify targets with abnormal heat signatures
- Equip your drone with a LiDAR camera to produce a high-density point cloud. To learn more about drone LiDAR, click here
- Capture multispectral data from beyond the visible light spectrum to give insight into agriculture and crop management
Drones and BIM
In construction and project management, drone surveying can provide critical data that goes hand in hand with Building Information Modeling (BIM).
At each stage of the construction process, high-resolution 3D photogrammetric or laser models captured by drones can be overlaid on and compared with pre-planned BIM objects. This allows for discrepancies between plans and reality to be identified.
Early detection of these issues can reduce construction error, omission, and re-work, and this project oversight has made drones an essential part of modern construction.

Overlaying BIM Models on a 3D Orthomosaic map
How accurate are drone surveys?
Before adopting drones into their workflows, many surveyors ask about aerial surveying accuracy. What degree of accuracy can drone surveying techniques achieve?
Surveying drone solutions can produce surveys with different degrees of accuracy, depending on the requirements of the project.
In an independent study by DroneDeploy, the DJI Phantom 4 RTK achieved 2 cm relative vertical accuracy and 1.20 cm relative horizontal accuracy.
For some applications, like checking crop growth, or construction progress, high relative accuracy is sufficient. For other jobs that also require high absolute accuracy, there are drones equipped with real-time kinematics (RTK) and post-processing kinematics (PPK) capabilities. When paired with a few GCPs, survey-level accuracy can be achieved.
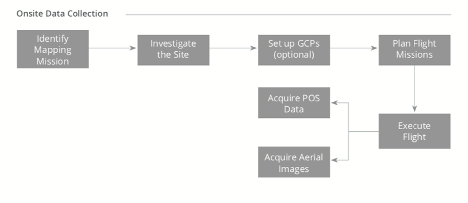
What does a typical drone surveying workflow look like?
Here is a graphic of how drones are typically integrated into your surveying workflows: Different drone solutions and drone-assisted workflows can offer different degrees of accuracy. When selecting your surveying drone, it is important to recognize your demands, the demands of your clients, and the tradeoff between speed and accuracy.
DJI’s drone surveying solutions
With all the benefits drones bring, and with so many surveying drone options to choose from, it raises the question, which is the best drone for surveying?
The answer ultimately lies with your priorities. Surveying accuracy requirements, data sensors, and cost should all come into consideration. Click here for more detail on the best UAV surveying and mapping solutions.
Source: https://enterprise-insights.dji.com/blog/all-about-drone-surveying
By Toby Knisely